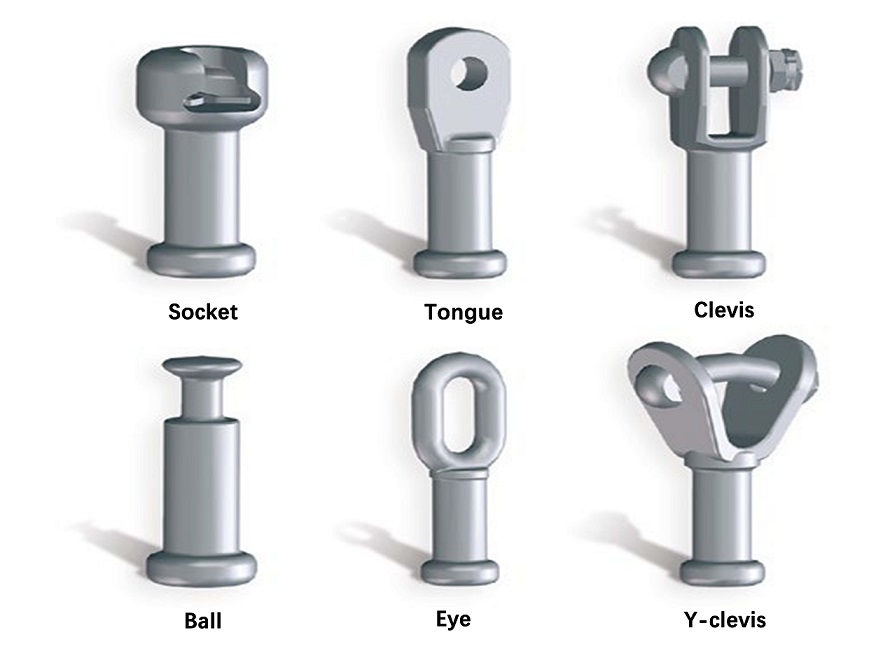
Typical end fitting configurations of composite insulators are shown in following figure. Dimensions are in accordance with:
- IEC 60120 -Ball and socket couplings of string insulator units – Dimensions
- IEC 60471 - Clevis and tongue couplings of string insulator units – Dimensions
- IEC 61466 -Composite String Insulator Units for Overhead Lines with a Nominal Voltage Greater Than 1 000 V - Part 2: Dimensional and Electrical Characteristics
- ANSI
- Others ...
For distribution level up to 70 kN, cast steel end fittings are used. For force ratings above 70 kN, forged steel end fittings are applied. For special applications such as railway catenary line fittings, a high strength coquille aluminium is often used. The steel end fittings are hot dip galvanized. The thickness of the galvanizing follows the recommendations of IEC 60383. Enhanced thickness for heavily corrosive in situ conditions or DC applications can be provided on request. Except above materials for end fittings, GW can aslo offter insulators with end fittings made of stainless steel.
Tests for end fittings of composite insulators
Mostly, a large quantities of end fittings are supplied one time so hence statistical methods are used to check the quality on a number of specimens which are considered to be representative of the supply. For composite insulators end fittings following tests will be taken before applied to manufacturing:
- Volume,
- Main dimensions,
- Steel composition,
- Hardness,
- Galvanizing thickness,
- Internal surface
Crimping Process for end fittings of composite insulators
The crimp machines used by GW to combine the end fittings with core of composite insulators have three independent integrated control mechanisms:
- Crimp pressure,
- Travel distance of moving jaws,
- Acoustic emission
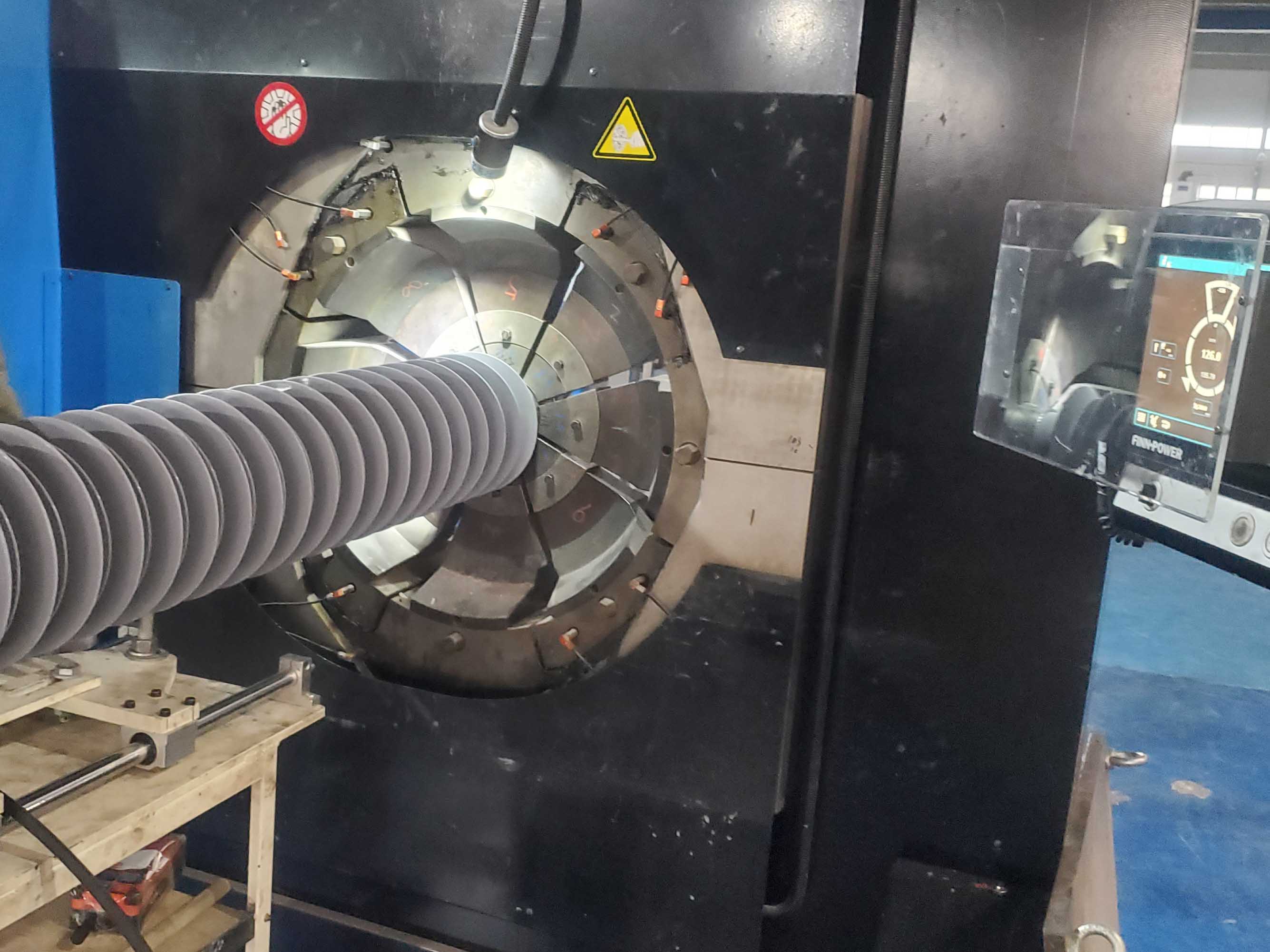

For each metal grade (steel, aluminium alloy, stainless steel etc.) and each combination of end fitting and rod diameters, an empirically established field of crimp parameters is applied. This will make sure the ECR fiberglass rod will not be broken, or get slip off with the end fittings of composite insulators.
When commissioning new machines, great care is taken in their calibration to guarantee the applicability of the introduced and well-established crimp parameters.